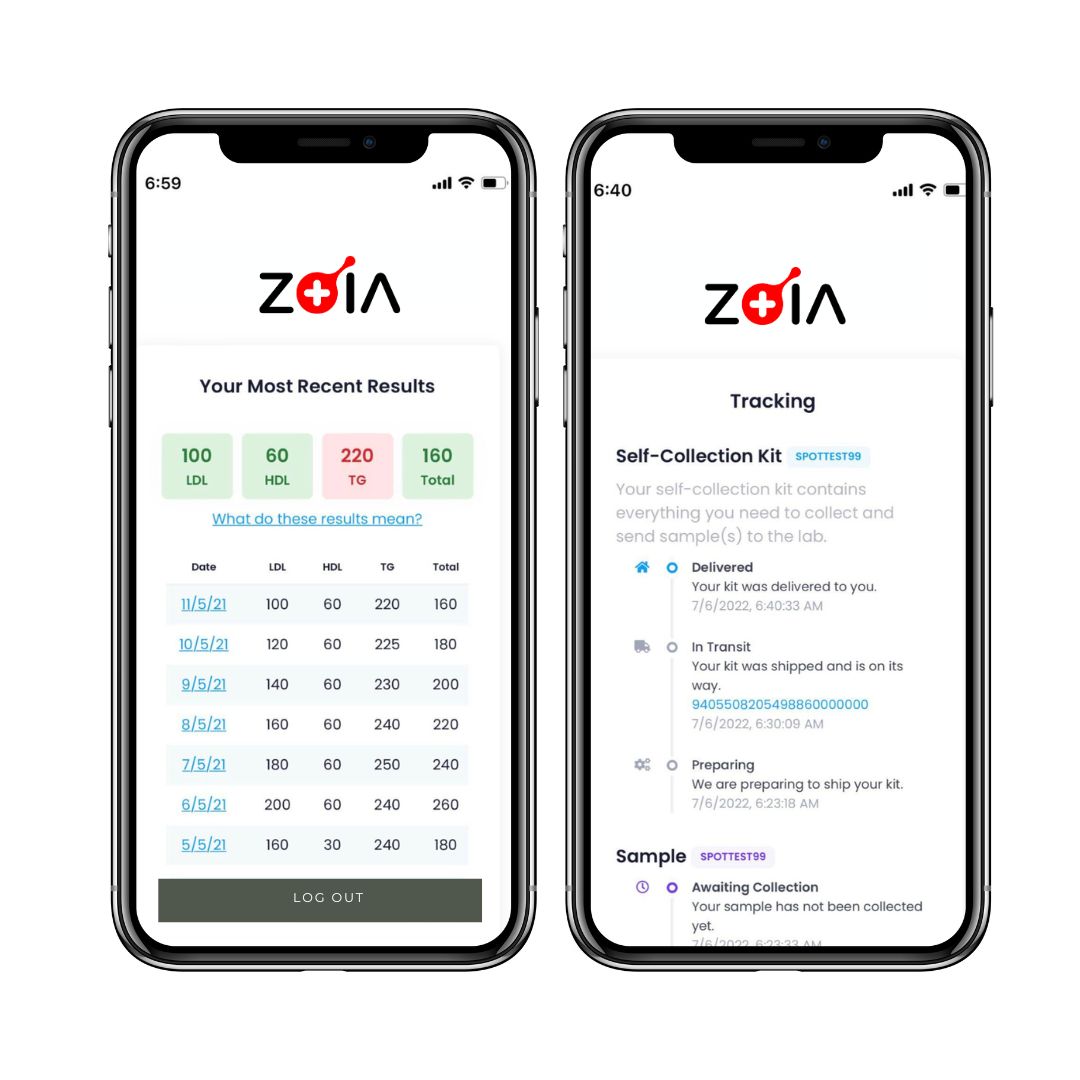
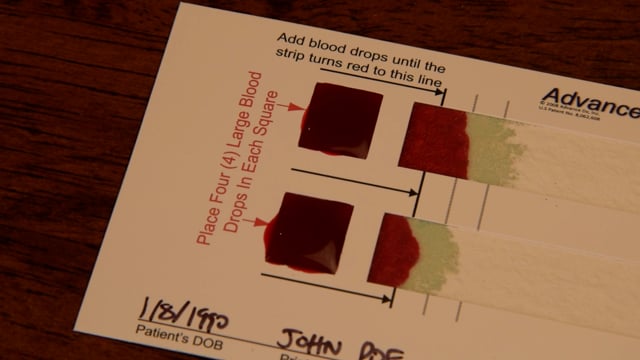
Description
About Test
A comprehensive women’s health panel blood test is a key component of preventive health care, enabling early detection and management of potential health issues. It provides a snapshot of a woman’s health, offering critical insights that can help guide personal and medical decisions for a healthier life.
A comprehensive health test for women can offer numerous benefits, helping to monitor and maintain overall health and well-being. Here are some key advantages:
Early Detection of Diseases: Blood tests can detect early signs of diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, liver disease, kidney dysfunction, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Cholesterol and Lipid Levels: Monitoring cholesterol and lipid profiles helps assess the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Managing cholesterol levels through diet, lifestyle changes, or medication can prevent heart attacks and strokes.
Blood Sugar Levels: Testing for HbA1c can help detect and monitor diabetes or prediabetes, enabling better management and prevention of complications.
Stress Management: This test provides insights into your Cortisol, Thyroid and Ferritin levels which are essential for overall health and energy.
Inflammation Markers: Biomarkers like C-reactive protein (hsCRP) can indicate inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic conditions.
Personalized Health Management: Regular comprehensive blood tests allow for personalized health plans tailored to an individual’s unique needs, improving overall health outcomes.
Peace of Mind: Knowing your health status can reduce anxiety and stress, providing peace of mind and empowering you to take proactive steps towards maintaining good health.
Consulting with a healthcare provider to interpret the results and create an appropriate health plan is essential for maximizing the benefits of comprehensive health blood tests.
• HbA1c: HbA1c is a blood test that is used to diagnose type 2 diabetes. It is also used to monitor blood glucose control in people with diabetes. HbA1c is short for glycated hemoglobin. The test is also sometimes called hemoglobin A1c. Hemoglobin (Hb) is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen through your body.
• ApoB: An ApoB test helps your doctor analyze whether or not you are at risk for heart disease. It measures the amount of apolipoprotein B in your blood. Apolipoprotein B attaches to negative types of cholesterol that cause plaque buildup in your blood vessels, which can lead to damage and heart disease.
• CORTISOL: Cortisol is a hormone produced by the two adrenal glands, which are located on top of each kidney. The pituitary gland in the brain regulates cortisol production. Cortisol plays an important role in the stress response. Maintaining an adequate balance of cortisol is essential for health.
• DHEA-S: Healthcare providers use DHEAS tests to measure levels of a steroid hormone that your body converts into estrogen and androgens (testosterone). A high test result may indicate an adrenal tumor or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), while a low test result may indicate Addison’s disease.
• E2: Estradiol (E2) is the hormone responsible for developing and regulating the female reproductive system, estradiol plays an important role in the menstrual cycle, supporting pregnancy and maintaining reproductive health.
• FERRITIN: Ferritin is a protein that stores iron for future use when the body needs it most. While an iron test gives the current amount of iron in your blood, testing Ferritin measures your body’s overall iron storage and determines if you have a healthy amount of iron in your body.
• HDL: HDL measures the amount of cholesterol found inside high-density lipoproteins (HDL) in a sample of your blood. HDL is often known as “good cholesterol” because it is associated with better cardiovascular health.
• hsCRP: This High Sensitivity test measures C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. (CRP) is a substance found in the blood that increases when there is inflammation within your body. Studies have shown that a single elevated hs-CRP level may be predictive of a myocardial infarction, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, and sudden cardiac death.
• HOMOCYSTEINE: A homocysteine test measures the amount of homocysteine in a sample of your blood. Homocysteine is an amino acid. Amino acids are molecules that your body uses to make proteins. High levels of homocysteine can damage the inside of your arteries and increase your risk of forming blood clots. This may increase your risk for heart attack, stroke, and other heart diseases and blood vessel disorders.
• INSULIN: This test measures the amount of insulin in a sample of your blood. Insulin is a hormone that your pancreas makes. It helps move blood glucose (blood sugar) from your bloodstream into your cells where it’s used for energy.
• LDL: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol is sometimes called the “bad” cholesterol because too much of it may clog your arteries with a buildup of plaque. Testing this helps determine how much LDL cholesterol is in your blood. This test can help you monitor your risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and other health conditions.
• TSH: This TSH test measures the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland. It prompts the thyroid gland to make and release thyroid hormones into the blood.
• TRIGLYCERIDES: Measuring triglycerides is important because triglycerides are a type of fat found in your blood, and their levels can provide critical information about your overall cardiometabolic health.
• ApoB/ApoA-1 Ratio: This test measures both Apolipoprotein A-1 (APO A-1) and Apolipoprotein B (APO B) as well as proving the ratio between them. APO B and A-1 are proteins which are involved in the body’s process of transporting and metabolizing lipids.
• EAG: Estimated Average Glucose. Knowing your eAG helps you know your blood sugar levels over time. It shows how well you are controlling your diabetes.
• ApoA-1: Apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) is a protein that has specific roles in the transportation and metabolism of lipids and is the main protein component in high-density lipoprotein (HDL, the “good cholesterol”).
Information
A comprehensive women’s health panel blood test is a key component of preventive health care, enabling early detection and management of potential health issues. It provides a snapshot of a woman’s health, offering critical insights that can guide personal and medical decisions for a healthier life.
When to test
A comprehensive women’s health panel blood test is a key component of preventive health care, enabling early detection and management of potential health issues. It provides a snapshot of a woman’s health, offering critical insights that can guide personal and medical decisions for a healthier life.
What's measured
A comprehensive women’s health panel blood test is a key component of preventive health care, enabling early detection and management of potential health issues. It provides a snapshot of a woman’s health, offering critical insights that can guide personal and medical decisions for a healthier life.
"NEW TO SELF-COLLECTED TESTING?
Learn How It Works
Take control of your health. Self-collected tests allow you to test in the comfort of your own home when it is convent for you.